Data types in C Language
Data types in C Language

What is a Data type ?
A Data type is a special word which is understood by the compiler that in which form the data is being stored. In other words, A data type is a to specify how we enter the data in our programs and what type of data we enter.
Every language has it’s own set of data types to handle the data we enter. There are two types of data types in C Language they are:
a) Primitive Data types (or) Primary Data types b) Referenced Data types (or) Derived Data types.
Primary Data types (or) Primitive Data types
These data types are considered as basic data types in C. There are 4 primary data types they are int, char, float, and void. Simply, a datatype defines which type of data to hold by a variable. Each data type has it’s own size of occupying space in the memory.
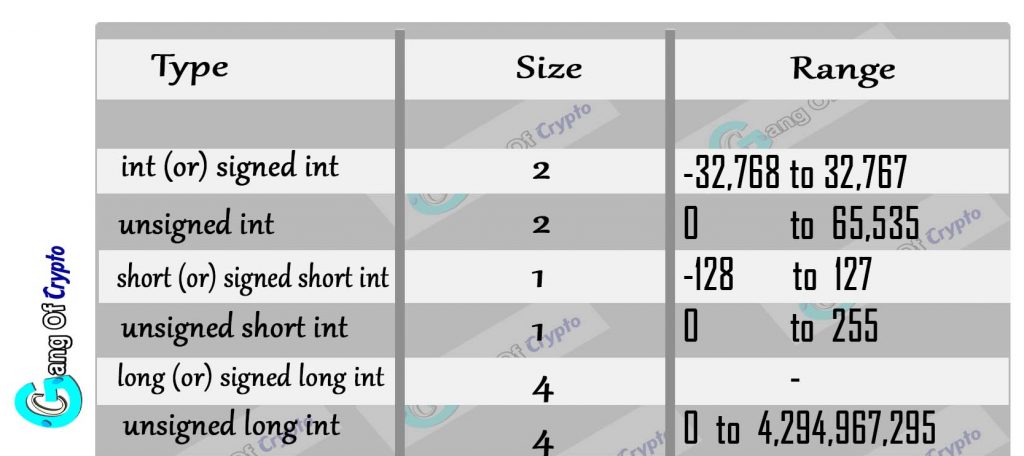
- Integer Type
Integer type are used to store whole numbers.
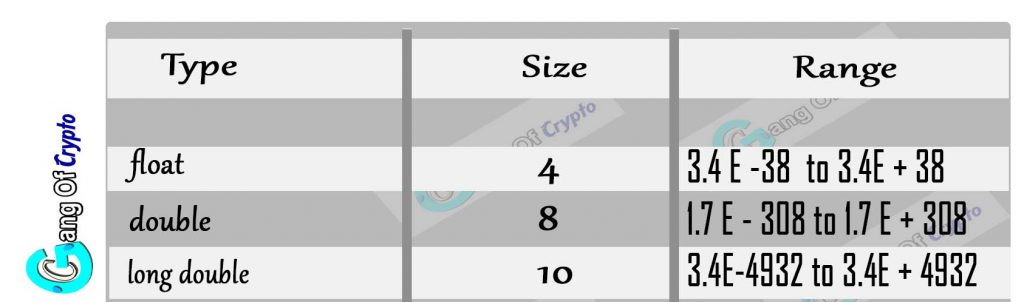
2) Floating Point Type
These floating types are used to store real numbers.
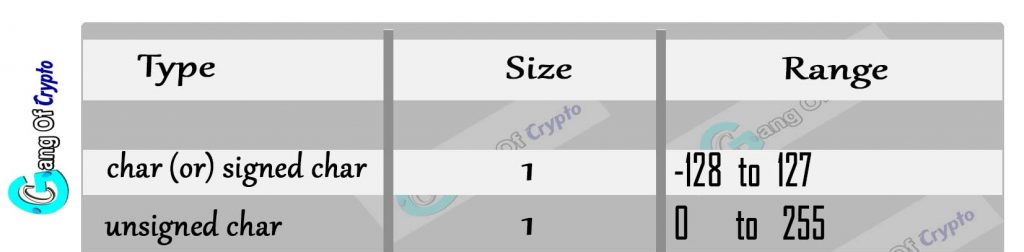
3) Character Type
Character types are used to store character value.
4) Void Type
Void means nothing (or) empty which actually means no value. It is used
when we need to return no value (or) NULL.
Derived Data types
Derived data types (or) secondary data types are the data types which are just like a extension of the primitive data types. For example, arrays, unions, etc. Which are complex than primitive data types.
Referred from here .
